Enterprise-level websites often have hundreds to thousands of landing pages. With so much content for Google to crawl, index, and rank, an enterprise SEO plan can be easily derailed.
Add in the multiple stakeholders that are involved in strategizing, executing, and communicating an enterprise SEO plan, and figuring out what went wrong can be a huge process.
But it doesn’t have to be. Although each enterprise website has unique business goals, the fundamentals of enterprise SEO are the same.
In this column, you’ll learn some of the most common reasons enterprise SEO may be underperforming. Check your own strategy against this list to find opportunities to improve SEO performance and ROI.
What Is Enterprise SEO?
Enterprise SEO can refer to both the size of an organization and the size of a website.
Larger websites are most often owned by larger corporations with established brand recognition and a wider market share.
But plenty of smaller brands have large websites and can benefit from approaching their SEO strategy through an enterprise lens.
If your website meets the following criteria, you need an enterprise SEO strategy:
- Large Size: Websites with a high number of landing pages or are owned by a large corporation or organization.
- Wide Reach: Websites that serve national or international markets and have a big market share.
- Brand Recognition: Websites from well-established brands that are perceived as an industry authority.
Reasons Why Your Enterprise SEO Is Underperforming
It may feel like there are hundreds of potential reasons why your enterprise SEO is not producing the desired results.
But ultimately, Google’s ranking factors can be boiled down to four key areas:
- Content.
- Technical aspects.
- Site authority.
- Page experience.
If you keep these high-level ranking factors in mind, you have a roadmap for how to audit your enterprise website, identify problems, and iterate on your enterprise SEO approach.
Content Considerations
1. Landing Page Content is Under-Optimized
Every year, Google gets better at understanding content relevance and quality. But with large websites, it can be quite the undertaking to ensure there is high-quality content on all of those landing pages.
In order to rank in search engines, your landing pages need to be in-depth, original, and have high content scores.
Also, they should also include rich media and good information architecture with components such as a table of contents, tabs, jump links, carousels, expandable content modules, and other interactive elements.
If you know your landing pages don’t measure up to Google’s quality standards, consider the following:
- Invest in content optimization software that can help you improve topical depth.
- Improve your information architecture with interactive design elements and features.
- Outsource your content creation or optimization to an agency.
2. Targeting the Wrong Keywords
If your pages are ranking but not earning traffic or converting, there is likely a disconnect between your target audience and target keywords.
It’s possible that you built your enterprise SEO strategy around keywords that no one is searching for, or keywords that are too competitive.
That’s why it’s best to take a blended approach to keyword targeting. Include a combination of short-tail and long-tail keywords in your keyword clusters.
Your landing pages should also target lower-difficulty keywords that you can rank for today as well as higher competition keywords that you can grow into over time.
3. Too Many Low-Quality Pages in Google’s Index
Due to their size, enterprise-level websites often end up getting low-quality pages in Google’s index.
When you waste your crawl budget on low-quality pages, you give Google the impression that your entire website is low-quality.
Sometimes, thin or low-quality pages are inevitable (particularly for ecommerce sites). To prevent those pages from ending up in the index instead of your money pages, take the following actions:
- Add “noindex, nofollow” robots tags to low-quality pages.
- Prune webpages that have low organic traffic and low organic search impressions and redirect PageRank to more valuable landing pages on your site.
4. Webpages are Too Similar and are Cannibalizing One Another
If your enterprise website has lots of webpages with similar content, not only are you competing with your competitors in the rankings — you’re competing with yourself!
Keyword cannibalization is common among enterprise-level websites with similar landing pages that are only slightly different but tailored to specific regions or markets.
Fixing this issue is simple. Either optimize your competing pages for different keywords or add rel canonicals.
![]()
If you choose the latter option, make sure the master version of the page has the highest-quality content and any similar pages are identified as copies.
5. Webpages Aren’t Conversion-Optimized
If your enterprise SEO content is earning your website new keyword rankings, impressions, and traffic but not conversions, focus your efforts on improving calls to action (CTAs) and the user journey.
A few conversion optimization ideas:
- Make submission forms simple and remove unnecessary fields.
- Add a chatbot to your enterprise site.
- Give users multiple chances to convert: I suggest a CTA for every two screen heights.
- Test full-page interstitial takeovers, driving users to your most important CTA.
- Add sticky banners for mobile users.
- Get extra conversions from your blog traffic by testing multiple CTA modules including inside your content and in the blog sidebar, footer, and header.
Technical SEO Problems
6. Site Architecture is a Mess
Enterprise websites can easily fall victim to site structure issues. With so much content, you need to clearly communicate the hierarchy of your website to users and Google.
This is essential to ranking well (and improving the user experience!).
To improve site architecture, make sure your site’s pages have useful, descriptive URL slugs that contain the keywords the pages are trying to rank for.
Also, avoid page paths that are overly nested and avoid hosting content on subdomains.
For example:
- Good: “website.com/category/page”
- Bad: “subdomain.website.com/category/subcategory/page”
Make sure your navigation menu provides access to the most important pages on your site.
Adding breadcrumbs also helps search engines understand your site architecture and helps properly distribute PageRank across your website.
If you haven’t submitted a sitemap yet in your Google Search Console Account, do so immediately.
7. Not Using PageRank to Your Advantage
When you link to another page on your enterprise website, you send along a portion of that page’s PageRank.
PageRank is the original metric that Google created to understand how much value or authority one page has over another.
If your enterprise website has lots of site authority, you likely have link equity that could be directed to boost other pages on your site.
The majority of link equity on your website will be on your homepage. For this reason, a pillar page model is ideal for enterprise sites.
Try using blog content to link back to your key service or category pages (which reinforces their importance in the eyes of crawlers).
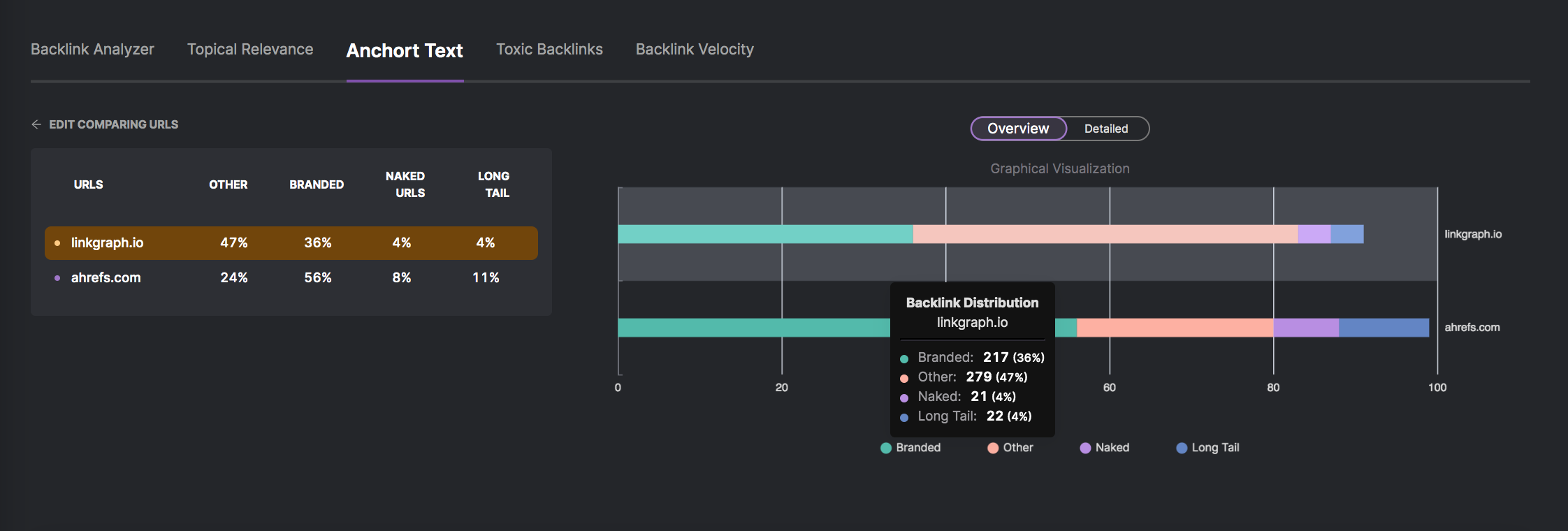
8. Making Mistakes with Anchor Text
If the anchor text of your internal links doesn’t align with the keywords you want to rank for, you’re hurting your chances of ranking for those terms.
Non-descriptive anchor text like, “click here,” “resources,” “more,” and others like it do not help Google’s crawlers understand what the different pages of your website are about or which are most relevant to users’ queries.
9. Broken and Low-Quality Links
If you have too many broken links, too many outgoing links to low-quality domains, or other linking issues on your site, Google quantifies your site as lower quality.
Use a site auditor or crawler tool like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog to crawl your site and take a look at your enterprise website’s external link profile.
If you see problems, repair your broken links or update your external links with more authoritative resources.
10. You’ve Maxed out Your Crawl Budget
Google has a specific crawl budget for how many landing pages it can and is willing to crawl. It’s very possible that your enterprise website has maxed out that budget.
In fact, a 2018 study showed that Google’s crawlers failed to crawl over half of the webpages of the larger websites in the experiment.
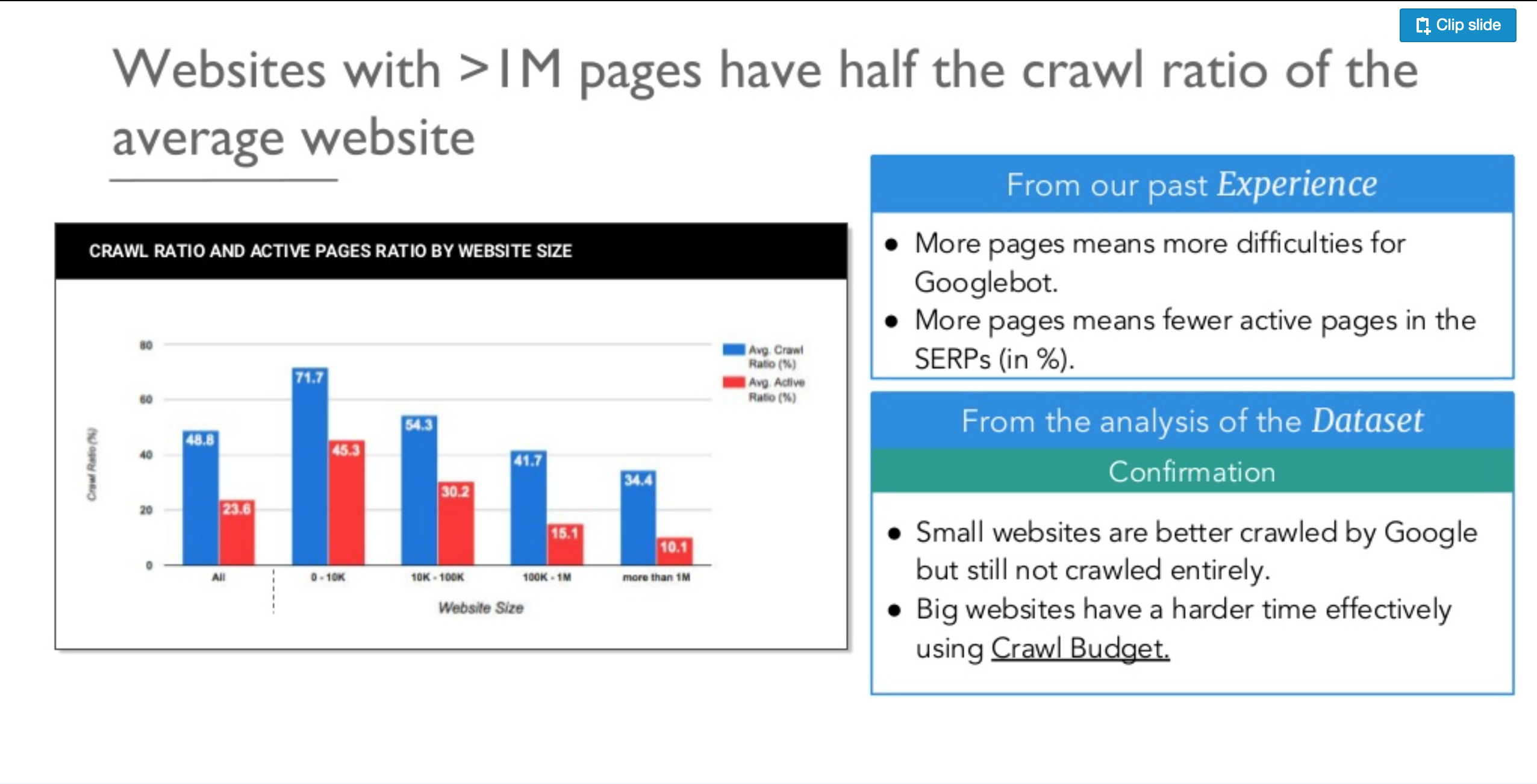
Crawl budget is a unique SEO factor that smaller websites just don’t have to deal with. So thinking about which pages you’re willing to spend your budget on is a major step in getting your enterprise SEO strategy back on course.
If you know a page doesn’t have ranking or conversion potential, don’t let Google crawl it.
Core Web Vitals & Page Experience Issues
11. Your Enterprise-Level Website Is Slow
There are a lot of moving parts to keep a large website running fast and they are essential to any enterprise SEO plan.
A slow enterprise website will completely undercut any and all enterprise SEO efforts.
Here are three levels of “slowness” that your enterprise website might be suffering from.
Server-side
Insufficient memory or CPU can result in slow database lookups for content on the page. The good news is that insufficient computing resources can be easily fixed by upgrading your web server with your hosting provider.
There are tons of WordPress plugins that can help with this as well and can fix those issues under the hood of your website with a single click.
Under-optimized assets
If images, videos, and other assets are not loading quickly or properly, Google will take notice. Try thumbnailing those assets to smaller, more appropriate resolutions, compress the images, or use a CDN to serve images to reduce load on your webserver.
Cloudflare provides static asset caching for free for anyone using them as a free DNS provider.
Client-side
For enterprise clients with a client-side to their website or heavy javascript modules, use CSS in lieu of JavaScript wherever possible. You can also bundle JS and CSS assets into individual compressed bundles.
WordPress plugins like WP Rocket let you take advantage of this if your web development team has organized your client-side javascript properly.
12. Poor Page Experience Metrics
With this month’s Page Experience update, the user experience and technical performance of your webpages are of even more importance.
Google’s Core Web Vitals is the new standard for page experience, and your enterprise website needs to measure up. Largest contentful paint, interstitial layout, and cumulative layout shift are all a part of Google’s ranking algorithm.
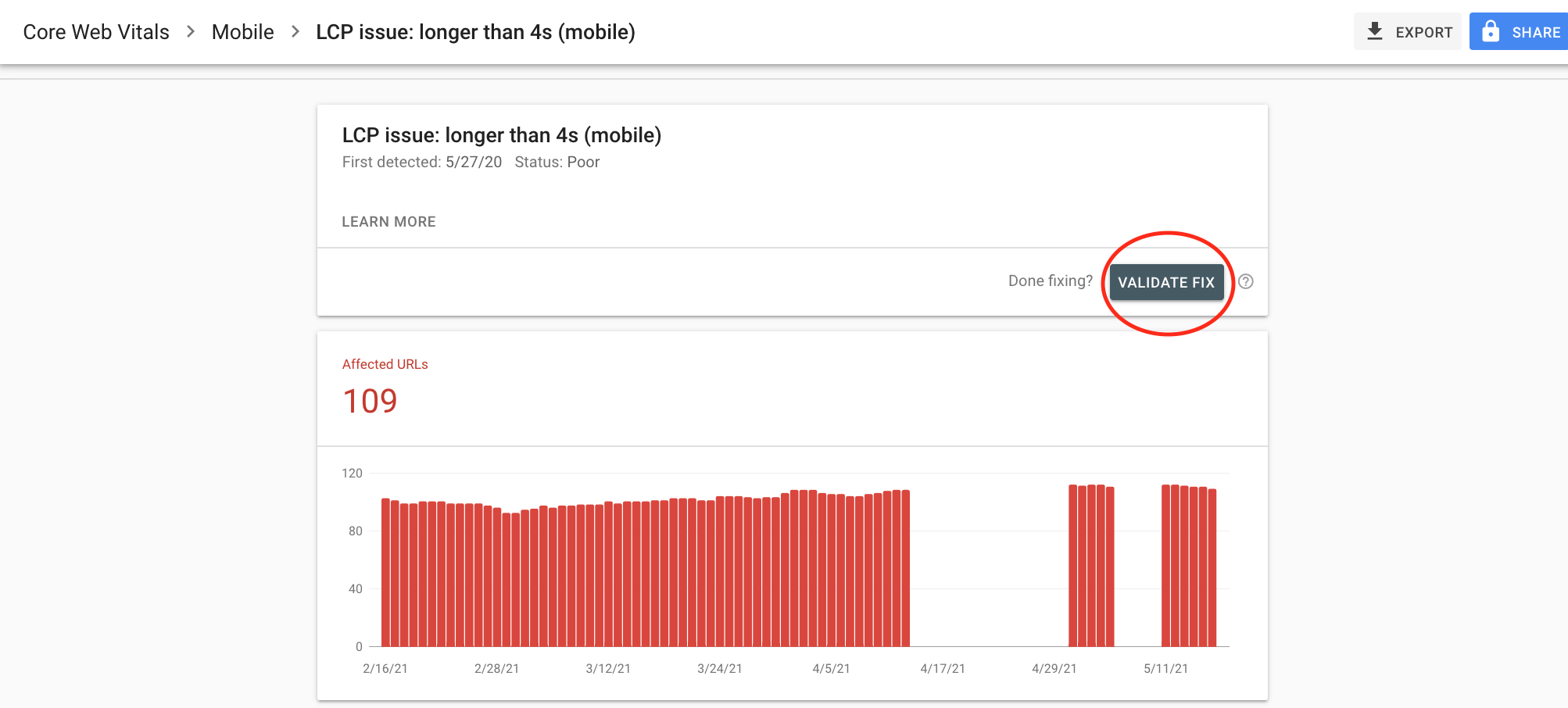
Not sure if your enterprise-level website meets these standards? Look at your Core Web Vitals report in your Google Search Console account for any errors or invalid URLs. Make the suggestions necessary to resolve those issues.
Once you have resolved them, submit a validation request in GSC. Google will let you know whether or not the issue is fixed.
Enterprise Authority Setbacks
13. Not Enough Site Authority
If you’re a smaller or newer company with an enterprise-level website, you might not have enough site authority to rank for top-competition keywords.
That’s why it’s important to have lower competition targets so you can make some small wins in the meantime until your authoritativeness improves.
Link building, public relations, guest blogging, content marketing, and a strong social media presence are all great ways to earn new backlinks and improve your site authority.
Earning new backlinks from quality websites should be a consistent part of your enterprise SEO campaigns.
14. You’ve Accumulated Toxic Backlinks
Enterprise organizations with strong site authority and larger backlink profiles may struggle to keep up with the links they accumulate.
They can also fall victim to negative SEO due to their established brand recognition and position as an enterprise corporation.
To avoid accumulating toxic backlinks that go unchecked, perform a quarterly backlink profile audit.
Submit a disavow file with those toxic links and stay up-to-date on the new links you earn.
Enterprise SEO Strategy Considerations
15. You’re Letting All of Your Content Rank (When It Doesn’t Need To)
Too many enterprise-level websites default to “index, follow,” robot tags on all of their pages. But not all of your content needs to be indexed.
What makes a landing page worthy of Google’s Index? Ranking potential + Conversion potential.
If a landing page on your enterprise website has thin content and is unlikely to rank well, don’t waste your crawl budget by letting Google crawl it.
Similarly, if the page doesn’t stand a good chance of converting, wouldn’t you rather have Google show a page to searchers that is more likely to turn them into real leads or customers?
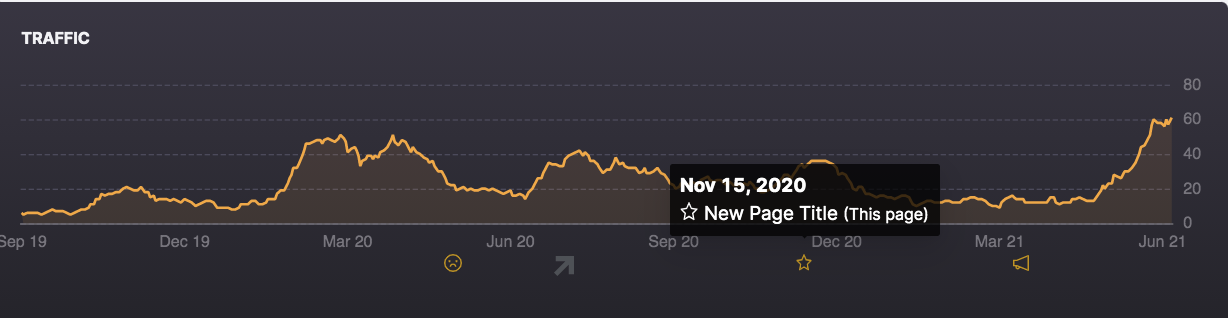
16. You’re Not A/B Testing Your Enterprise SEO Optimizations
Getting to the first page can usually be accomplished by following SEO best practices, but getting to the top spots for highly competitive keywords takes more nuance and granularity.
Try SEO A/B testing specific optimizations on your webpages like page titles, meta descriptions, internal links, content length, and other elements.
Google Search Console’s comprehensive and daily keyword tracking will make accurately tracking your SEO A/B tests easy.
17. Your Enterprise SEO Tracking Is Incomplete
It’s possible that your enterprise website is ranking and performing better than you realize.
Depending on the keyword rank tracking software you’re using, you may not be seeing all of your organic keyword rankings.
Many popular SEO software use bots to scrape the SERPs to gather ranking data. But those bots crawl a limited number of SERPs, and not at the same rate.
For that reason, Google Search Console is the only true measure of your SEO performance.
Remember that SEO takes time.
Metrics like increased total number of keyword rankings, average rank position, and impressions can give your enterprise website a better sense of the small wins you are making right now with your enterprise SEO plan.
Final Thoughts on Improving Your Enterprise SEO Performance
Any good SEO plan requires iteration, so don’t be discouraged if you’re still identifying where to right the ship.
Making small changes, measuring their impact, and redeploying the most effective strategies will help you get your enterprise SEO campaign to deliver more consistent results.
More Resources:
- How Enterprise SEO Can Maximize Traditional Marketing ROI
- 11-Point SEO Checklist for Enterprise Internal Link Optimization
- Enterprise SEO Guide: Strategies, Tools, & More
Image Credits
All screenshots taken by author, June 2021.





