Editor Note: The author has no affiliation with any of the plugins mentioned, but did solicit plugin recommendations from the Magento community, which allowed some developers to recommend their own tools.
When I started my career in the digital tech space, I was leading business development for a web development firm. I used to talk to my clients about Magento, the high performing e-commerce engine, when we talked about developing online stores for their brick and mortar businesses.
Even then, we had to have dedicated Magento developers to really get behind the platform and manipulate it properly. The business development team would often run into cases where a potential client’s site had already been developed in Magento, but we could see the back-end was riddled with bugs and there was much-needed Magento know-how to apply. Fixing the Magento messes of others was at times the only nature of a contract.
Now that I’ve moved out of the web development space and am focused on marketing and search engine optimization, I am seeing another side of this coin: clients with Magento sites riddled with common SEO problems.
 Source: Wikipedia
Source: WikipediaThe WordPress of eCommerce, Magento is an open-source platform for online stores and developers who can add to it, modify it and build on it as needed. Many extensions and plugins have been built allowing site owners to personalize and enhance their Magento websites. Purchased in 2011 by eBay for $180 million, Magento is not a newbie in the online sales space.
While Magento is still a powerful solution for e-tail operators and e-commerce developers, SEOs who have had any onsite experience with the Magento back-end are familiar with and have wrote about the aspects of the platform that are not SEO friendly. In fact there were a number of “8 SEO problems found in Magento” blog posts that came up in my research and I wasn’t surprised that others had already looked into what I perceived were standardized SEO concerns built into Magento’s platform.
 Screenshot of February 1st, 2015 Search Results
Screenshot of February 1st, 2015 Search ResultsAccording to Shero Designs, there are plenty of default settings in Magento that if left untouched, can lead to a list of SEO concerns. Magento is available as a free open-source e-commerce platform, known as their Community Edition and also as a paid e-commerce platform, which is their Enterprise Edition.
Open source means developers can access and build upon the source code. Many developers have dedicated time and resources into developing Magento extensions to improve upon the platform’s SEO performance, but they will cost you.
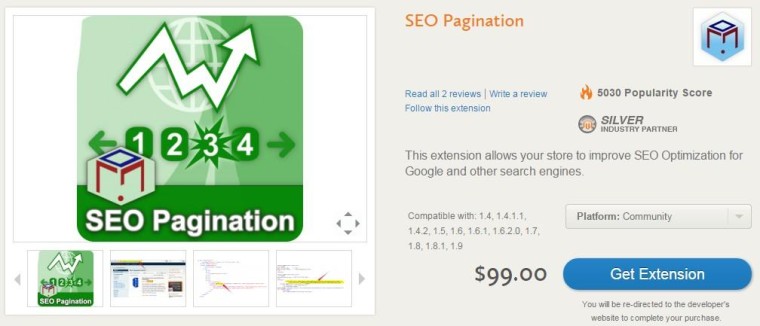 Screenshot from Magento Connect
Screenshot from Magento ConnectYou can see on the right-hand-side of the image above, there is a drop-down menu that reads “Platform: Community”. Here you can select which version you need to use this extension. The Enterprise Edition has additional resources available to make your online store more SEO friendly, but this version too relies on extensions like the one featured above to improve on major issues like Pagination for search engines.
While some may argue that the Enterprise Edition has full page caching allowing improved website speed and better SEO performance, Magento SEO Expert Paul Rogers, says the SEO side of Magento is exactly the same between the Community and Enterprise Edition. He adds that while the full page caching in the Enterprise Edition won’t offer significant SEO value, there are some Magento-specific site speed improvements that can eliminate the risk around performance and recently published a guide about this.
Yoast is working directly with Magento developers and released a Magento SEO Guide in 2013 recognizing the growing SEO concerns amongst the web community. The guide provides detailed instructions for how to optimize your Magento set-up in three main categories. The first two, Basic Technical Optimization and Magento Template Optimization, focus on Magento-specific configuration. The last category, Advanced Magento SEO and Duplicate Content, is where the real onsite SEO action happens.
The Biggest Downer is Duplication Management
SEOs operate in a vacuum to a certain extent doing the best we can to follow the rules of our captor known as Google and sometimes Yahoo! or Bing (traffic shares have been going up). While the whole gambit of offsite “relationship building” remains an enigma to most still, onsite optimization is still a hard science.
There is a firmly set road map that makes a website crawlable or not to Google bots. In the case of Magento websites, there are many SEO areas that require tweaking, configuration, know-how and likely the implementation of a purchased extension. The area of Magento’s e-commerce platform most likely to harm to your site is its potential to produce duplicate content pages. Yes, this is also true for some of the other e-commerce platforms as well.
Ben Oren published an article last month on SEJ talking about 8 Advanced On-Page SEO Techniques. The third area focuses on duplicate content. Having duplicate content, Ben says, won’t necessarily lead to a penalty but it can lead to devaluation among an already competitive search landscape. Let’s breakdown the major SEO pain points when it comes to duplicate content and see how Magento can comply.
It All Comes Down to Canonicalization
The biggest duplicate downers to deal with in Magento are almost all related to problems of canonicalization. Defining a primary URL to represent one unique piece of content is done through the process of ‘canonicalization.’ Moz provides the following definition and explanation for canonicalization as it pertains to SEO:
“Canonicalization for SEOs refers to normalizing (redirecting to a single dominant version) multiple URLs… The fundamental problems that canonicalization can fix stem from multiple uses for a single piece of writing–a paragraph or, more often, an entire page of content–that appears in multiple locations on one website or on multiple websites. For search engines, this presents a conundrum: Which version of this content should they show to searchers? SEOs refer to this issue as duplicate content. To provide the best user experience, search engines will rarely show multiple, duplicate pieces of content and thus, are forced to choose which version is most likely to be the original (or best).”
The process of canonicalization allows e-commerce website owners to tell search engines where the primary URL is for any duplicate pages. Canonicalization solutions can take different forms, mainly through 301 redirections, through canonical tag insertion (add code) or through a robots.txt file.
In this sense I’m referring to canonicalization as a larger theme of SEO issues that pertain examples of the duplicate content conundrum referred to in the Moz definition above (not just the canonical tag!). The common forms of the canonicalization conundrums present in Magento are broken down below:
Area: Session IDs
Some sites are set up to assign as session ID to each visitor. Session IDs are a common cause of duplicate content issues. Session IDs allow online store owners to track the visitors behavior on the server, without any personally identifiable information being tracked. Multiple versions of the same page will be created if the users session ID is stored with the URL. For example you will have the same content on both of these pages:
www.website.com/category
www.website.com/category?sid=32109
Problem: Many e-commerce website content management systems use sessions IDs in the URL to track users.
Solutions:
- Use a cookie to track user sessions instead of a session ID
- Canonicalize URLs for each URL with a session ID
- Deindex session ID URLs via robots.txt
Available Extension: MageSEO
Area: Internal Search Results Pages
Internal search pages are created by the server when a visitor uses the search bar to look for something. These internal pages might get indexed by Google if no action is taken and will be considered duplicate content competing with Google’s own search results. Matt Cutts his expressed his disinterest in having a website’s internal search pages showing up in Google’s search results back in 2007. While internal search pages can be problematic from an SEO point of view for Google, more and more site visitors rely on the search bar within e-commerce sites to find the products they’re looking for, says a Marketing Sherpa study cited by Blue Acorn.
Problem: Internal search pages are dynamic pages, which aggregate existing content.
Solutions:
- Set up search results pages in noindex
- Disallow those pages through robots.txt
Available Extension: MageSEO
Area: Duplicate URL Pathways
When a single product is placed into two different product categories (ie. “on sale” category and also in “last season’s collection” category) in your Magento store, its possible the two URLs will be created for the same product. The actual breadcrumb navigation can present the same product on different levels of the site.
Problem: You can end up with two different URLs for the same product (which may also create an issue for your breadcrumb URL navigation displays):
http://www.yourboutique.com/category1/product1
http://www.yourboutique.com/category2/product1
Solutions:
- Configure your URL structure to get ‘product’ as the root directory for all your products (ex: http://www.yourboutique.com/product1)
- Canonicalize URLs so they point to the best, most powerful or the most relevant URL. If you want to preserve your main category pages, use canonical tags to point to the main URL.
Available Extension: Most Magento SEO extensions can help with this, but recent versions of Magento allow site owners to correct this issue manually anyways. I also just got word of an extension about to hit the market that will fast track this process with a focus on discontinued products (updates in the comments section to come).
Area: Pagination & Layered Navigation
Pagination occurs when an article or category spans multiple pages and are split over separate URLs. Because page 2,3,4, etc can be very similar to the first page, these often generate near-duplicate content. The content is very important for SEO however, as these are often the only links available to products which don’t get listed on the first page.
These are not copies of the first page, but titles and meta information will inevitably be very similar, and so they can be seen as low quality. You can choose to display all your products to avoid this issue of pagination, but depending on the number of products, this could decrease the page loading time.
Layered Navigation is different from pagination because visitors search by product attribute rather than the number of pages, but it still causes the same types of problems.
Problem 1: Pagination filters can create near-duplicate or low-quality URLs and may dilute your SEO authority.
Solutions:
- Display all the products in the code and use Ajax or HTML 5 as a layer to display the products to the users the way you want.
- Use rel=prev, rel=next tags to make sure your SEO authority is concentrated into the main URL.
Available Extension: SEO Pagination
Problem 2: Duplicate Product Listing Via Filters
Visitors like to search by product attributes, but this layered navigation is brutal for generating a lot of duplicate content. Paul Rogers stated in an interview that the most common SEO problem he comes across in Magento websites is “definitely indexation of layered navigation (and internal search pages being indexed).” The point being you can’t let Google index your layered navigation pages. It is common practice to filter products by other attributes than categories: ex: price, recency, etc. This is problematic because you display the same content in a different way and the URL usually ends up with the filter parameter (ex: filter=price)
Solutions:
- Canonical filter URLs to the main URL
- Use Ajax or HTML5 to display filtered products without changing the main URL
Available Extension: Magento Layered Navigation Pro
Problem 3: Number of Products Viewed per Page
Pagination can be set up using page numbers or using a bracket of products displayed. For example it’s common to see filters that allow you to view 10 products or 50 products at a time and often a “view all products” option as well. This creates a problem of URLs displaying similar content, a first cousin of major canonical duplicate content issues if you will.
Solution: Display all the products in the code and use Ajax or HTML 5 as a layer to display the products to the users the way you want.
Available Extension: There is no extension for this, rather it requires a developer to implement the solution recommended above.
Expert SEO Notes on Canonicalization
301 redirects force the user or bot from one URL to another, and passes almost 100% of the ranking authority from the old URL to the new. Canonicalization tags do not move the user or bot from one URL to another, but make a suggestion to bots that the proper home for the content is at the URL contained in the canonical tag. If honored it will move ranking authority to the canonical URL. Website owners could also choose to ‘eliminate’ the content from the search engines eyes by adding a robots.txt directive instructing search engines to not crawl specific URLs and adding meta noindex tag, which will instruct search engines not to include the URL in their index.
The canonicalization tag is not a directive, it’s a hint, and Google does not always choose to honor it. In cases where the canonicalization tag has been incorrectly used, it lessens the chance the tag will be honored.
Non-Canonical Duplicate Issues
Duplicate content that occurs across multiple domains gives search engines the added challenge of trying to attribute content-ownership to not only the best page on a site, but the best page among many sites. SEOs need to account for both.
If our site content ends up on other websites, and those other websites have more authority than ours, they can easily end up outranking us. If we have duplicate content on our own site, the ranking authority can get split between the page versions and reduce our chances of ranking any one version. The official Google Webmaster Central blog has an explanation of canonical issues and their proposed solution using the canonicalization tag.
Area: Product Feeds
Product feeds allows you to publish and update your list of products on third party websites like Shopzilla or Amazon. This gives you an opportunity to tackle different marketplaces, but might be a headache for your SEO department. Indeed, websites like Amazon have a lot of authority and likely outrank your own product pages on SERPs.
Problem: The problem is that third party site description of the product will duplicate your own website’s description if not properly managed.
Solutions:
- Create a different product description for the product feeds
- Create a kick-ass and rich description for your product pages. Don’t use the merchant description, especially if the merchant has its own website (ie. You resell Bic pens on your pensareascoolashens.com website. Make sure you don’t use the same product description that Bic has on their site! Make your own product descriptions and even have fun doing it, speaking to your unique audience).
Extension: There is no magical Magento extension for this duplicate content issue. All that is needed is an extension of your common sense mixed with some imagination and the time invested in writing unique content.
Concluding Commandments: Make Sure You Consult a Professional
Implementing the solutions to these common duplicate content issues in Magento may or may not be straightforward, depending on your current situation or your client’s. I cannot stress enough the importance of working with dedicated Magento specialists and SEO experts to implement both development and SEO-based tweaks and fixes. If you are about to open a Magento store, you can save yourself a lot of cleanup and messy indexing if you simply take the time to configure your URLs properly now.
I heard this saying on a home building show the other day, but I think it also applies to site configuration as it pertains to SEO:
No one has time to do it right the first time, but everyone has time to fix it.
Consider costs down the line and loss of marketing momentum if you don’t do it right the first time. Take the time to configure your store properly now, and search engines will thank you for it.
I would like to extend a special thanks to Paul N. Rogers, Sarah Benmaza, and Naoise Osborne for their contributions to this post.
Feature Image via Raumrot (CC-Licensed)





