Google published a post on the Inside Search Blog back in February 2012 citing 40 key changes they had made to their search algorithms during the last month.
Among these 40 algorithm updates were projects codenamed Nesehorn (affected flight queries), rich snippets (were expanded worldwide), and another update that changed a major aspect of local search forever: Venice. From the blog post:
“Improved local results. We launched a new system to find results from a user’s city more reliably. Now we’re better able to detect when both queries and documents are local to the user.”
Fundamentally Google has, and always will be a document retrieval system that aims to satisfy user search intent and needs.
The Venice update showed that Google understood that users (at times) wanted search results relating to products and services with a closer geographical proximity to them by increasing the frequency and volume of local hybrid results.
The Impact of Google Venice
Before Venice, Google used Google Places as a feature within search results to show users localized content.
But with Venice, the traditional “10 blue link” results also began to cater for local intent.
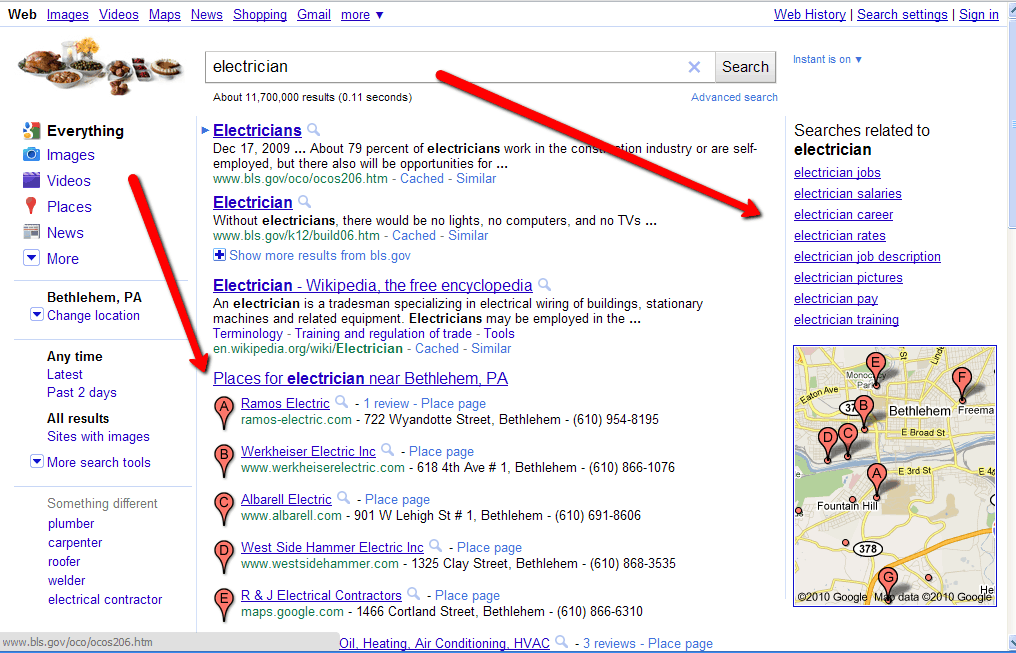 Back in 2012, before Venice, the Map Pack and Knowledge Graph, how the search engine displayed localized content was a lot different.
Back in 2012, before Venice, the Map Pack and Knowledge Graph, how the search engine displayed localized content was a lot different.Local intent is clearly defined by queries such as [X near me] or [X in town], but some queries can have a local intent even though it isn’t so clear. In the past when users made queries without a dominant search intent, but multiple common (and some local) Google will have returned a SERP based on optimization.
With Venice, Google now included search results based on either the physical location you had set (something you could do back in 2012), or based on your IP address.
Venice also opened the doors to smaller businesses and brands, giving them the opportunity to rank for bigger marquee, short-tail search phrases.
Typically, larger brands with big budgets and advanced SEO campaigns were able to monopolize the top ranking spots for these high-value keywords (with some exceptions).
Organic Listings vs. Google Places
But thanks to Venice, along with the correct local search optimization, smaller brands and businesses could compete for some of the bigger search volume keywords if they had, or could possess a local intent.
Having microsites and landing pages for specific areas that you served became even more important with the Venice update, and through using the correct combinations of [location] + [target keyword] (and a number of other SEO factors) you were able to gain a foothold on page one without necessarily having a bricks and mortar location, or registered business address in that area.
The Venice Update also saw homepages for big national firms competing with localized pages from smaller businesses on Page 1 of Google.
Venice Didn’t Stop Local Spam
However, the Venice update also gave increased focus to local SEO, and the spam tactics used by some to try and gain higher rankings. Examples of these tactics (still utilized today) are location stuffing and doorway pages.
 In some verticals, stuffing a page with a list of town names still brings benefits.
In some verticals, stuffing a page with a list of town names still brings benefits.Spam Still Works
On a lot of local niche queries, spam still works and performs well.
In October 2017 via Twitter, fellow digital marketer Mark Preston raised a query with Google’s John Mueller when a lorem ipsum website was appearing on Page 1 for one of his business’ commercial keywords.
… also, 2) the query is really rarely used, not a lot of people see that result, it’s unlikely the spam team would take manual action.
— John ☆.o(≧▽≦)o.☆ (@JohnMu) October 11, 2017
For extremely niche and low volume search queries (which make up a lot of local searches), Google scrutinizes the queries and search results pages less, as the time and resource can be better spent on queries that more people see and search for.
All of this is not to say any query isn’t important, but assuming 1-3 people/day (guessing) sometimes see this, it’s really, really niche.
— John ☆.o(≧▽≦)o.☆ (@JohnMu) October 11, 2017
It’s also important to remember that in a lot of local verticals, there are a large number of old websites that were developed a long time ago and haven’t changed much. There’s also a high chance that there isn’t a lot of high-quality content in the vertical.
2 things: 1) there’s not a lot of good content to rank for that query, in which case we sometimes dig up weird things.
— John ☆.o(≧▽≦)o.☆ (@JohnMu) October 11, 2017
This can be frustrating as in many cases the spam isn’t even subtle, yet it still ranks highly on Page 1 of Google.
The variables that Google uses to assess quality are also weighted differently than the regular “10 blue links”, and quality is a subjective notion.
Local SEO Since Venice
Since the Venice update, local SEO has continued to evolve and adapt to both improving user quality and demoting spam tactics.
Google Plus & Google My Business
When Google Plus launched it effectively replaced Google Places as the go-to for businesses to gain a foothold in local search results.
Google Plus Local effectively challenged businesses to be more social, by posting regularly to their dedicated Google Plus page, as well as engaging in Hangouts, posting events, and encouraging customers to +1 their pages.
Google My Business was then rolled out (and replaced) Google Places, followed by the Map Pack, which uses the same variables as local SEO but weights them differently.
Pigeon & Possum Updates
In more recent times, Google have taken further steps to improve the results appearing in the Map Pack for users, as well as targeting duplication and spam.
Image Credits
Featured Image: Shutterstock image modified by Danny Goodwin with Canva
2012 Results Screenshot, sourced from Google Images
Other screenshots taken by Dan Taylor





