I recently interviewed Sagar Kamdar, Google’s Director of Product Management on Search, who is responsible for their Authorship program and their other “social initiatives” in search. In this Q&A, Kamdar shares how Google’s search results pages have evolved to better attribute authors and websites to content. He also responds to some questions on many search marketers’ minds, including, “Are there now improved ranking opportunities with Authorship to take advantage of?”
I recently interviewed Sagar Kamdar, Google’s Director of Product Management on Search, who is responsible for their Authorship program and their other “social initiatives” in search. In this Q&A, Kamdar shares how Google’s search results pages have evolved to better attribute authors and websites to content. He also responds to some questions on many search marketers’ minds, including, “Are there now improved ranking opportunities with Authorship to take advantage of?”
Google Authorship: Connecting Writers and Content Owners with Audiences
Authorship is considered to be one of Google’s “social search” efforts. Basically, it allows Google to verify the author of a Web page by having it point back to their Google+ profile page, which requires just a few verification steps and the insertion of a rich snippet on the Web page. When done right, it’s your mug showing up in the Google SERPs when people search for content that you’ve written.
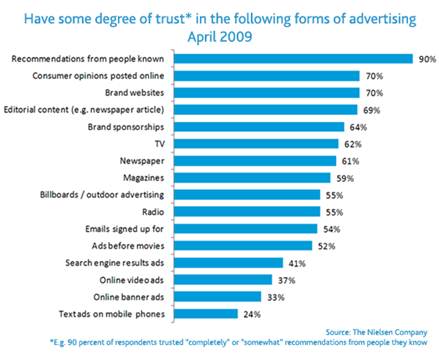
Kamdar explained to me that the Authorship program was based on the premise that content associated with a real identity is often of higher quality than content published anonymously. Backing this up is a Nielsen survey taken in 2009, which showed that the people we know score the highest in terms of trust with 90 percent of total survey respondents, in comparison to only 41 percent trusting search engine results.
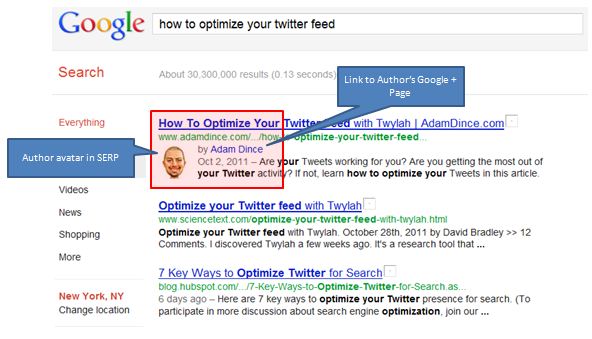
A great benefit with Google Authorship is the image thumbnail feature. You don’t have to be an Image SEO expert to know that photos in searches are especially good because people tend to click on them more.
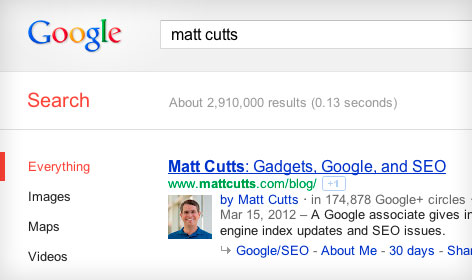
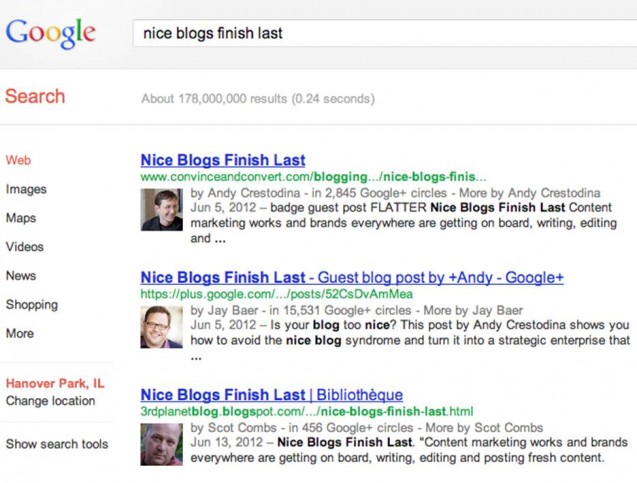
Of course, one of the important reasons that Google implemented the Authorship program is to help them identify duplicate content. Some authors have had problems with others ranking higher than them in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) for their own original content. Authorship is supposed to push the original author to the top of the rankings when someone does a search for their article. What it can’t yet do is exclude others who aren’t the original authors, as the screenshot below of an original article by Andy Crestodina of Orbit Studios shows.
Q&A with Google Authorship’s #1 Authority, Sagar Kamdar
How long has the Authorship program been around, and how big is it today?
The Authorship program started on June 28, 2011, a little over a year ago and with just a few authors. They now report to have hundreds of thousands of authors participating. “We’re still in our pilot phase as we’re learning a lot from authors and users as we continue to look for ways to improve the program,” says Kamdar.
Is Authorship used by Google as a ranking signal? (i.e., does it factor into search rankings?)
Not for now, but it isn’t off the table. “We use over 200 signals to determine search ranking, and although authorship is not currently one of those signals, we hope to experiment with using information about authorship as a signal in ranking in the future,” says Kamdar.
That being said, Kamdar stressed that while Authorship is not an algorithmic factor, it is a strong contribution to their social signals that are used to weight search results, including social activity outside of Google+. “We’re working on a number of signals to identify high quality authors,” he says.
How long does it typically take for Google to make the connection?
Kamdar explained that once an author is set up correctly, the timing depends on when they recrawl/index the content.
Does Google provide a way for someone to check out their Author rank “score?”
Not at this time. Other SEM bloggers have been sharing their own programs for mining Author data for link building, like AuthorCrawler, along with other tools for identifying key influencers in an industry, such as Followerwonk, Topsy and FindPeopleonPlus. These are all experimental tools used for scaling data. No case studies have appeared yet to show a direct cause-and-effect relationship with Authorship.
Does Google allow for authors to submit a “feed” of their articles for inclusion in the Authorship program?
Not at this time.
Is there a way to check which articles have been crawled and indexed that have been set up for Authorship?
Only in manual search. “We show all the articles we have crawled and indexed that have been set up for authorship,” says Kamdar. “Often times when an article is missing, it’s because authorship wasn’t set up correctly on the content, or we haven’t recrawled/indexed it since it was set up.”
How can someone get all of their previously published articles into Google Authorship?
There are many content creators who’ve already published hundreds of articles. How can they get their past articles on both their own website and websites they are guest contributors for to show up with their author identification in Google search results?
“The most important thing is to make sure on any new content you write you’ve set up authorship correctly,” says Kamdar. He recommends doing these two things:
- Email/Google+: “If you have an email address on the domain you write for, it’s best to verify the email address, and we’ll attempt to link all the content on that domain with your Google+ identity,” says Kamdar.
- Footer/Header Verification: “On most content management systems, there’s a common footer/header on each article. If people can configure the footer or header to set up authorship correctly, it’s a relatively painless task to get set up,” says Kamdar. You can see some examples with Mashable’s Ben Parr and GigaOM’s Mathew Ingram.
What does Google recommend for further information?
Kamdar personally recommends that those who are looking to participate in Authorship check out these resources:
- Sign-Up Tool: Use the sign-up tool located at https://plus.google.com/authorship, which Kamdar says has now been simplified with easier-to-follow instructions.
- Webmaster Tools Help Article: Read the help article entitled Author Information in Search Results. “We have made many changes to our help article to make things simpler to understand on how to get set up,” says Kamdar.
- Rich Snippets Testing Tool: Currently in beta, this tool will give you immediate feedback on whether you’ve set up everything correctly.