How important is schema markup for local search engine optimization (SEO)?
Most local SEO experts and webmasters are familiar with the impact of having well-optimized SEO elements on their landing pages, such as optimized title tags, well-written content, and more.
However, what exactly can you accomplish by applying schema markup to your local business website?
Quite a bit, actually.
When it comes to organic search, there are several reasons why having a proper and thorough schema applied to your website is a substantial competitive advantage.
In fact, it’s been reiterated by Google time and time again that schema helps search crawlers do their job more effectively by helping them comprehend a landing page and delivering relevant information in the SERPs.
In this post, we will share a few recommendations to help your local business get the most out of using schema to boost your local SEO.
First, let’s start with defining what exactly schema markup is.
The Difference Between Schema, Structured Data & Rich Results
The terms “structured data” and “schema” are often used interchangeably in webmaster and SEO verticals.
However, before we dive into the recommendations it’s helpful to know the semantic differences between these terms.
Structured Data
Google defines structured data as “a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content.”
To put it simply, this format was developed to help search engines accurately understand a webpage to properly display snippets of information in the search results pages.
Schema
Schema is a form of structured data that was officially launched via schema.org.
Schema was created via a collaborative project by all the major search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing, and Yandex) in 2011.
Utilizing the markup available on schema.org enables a landing page to be eligible for rich results.
Rich Results
Rich results (formerly called rich snippets) are any extra information you see in the search engine results pages (SERPs) that are beyond the atypical blue title tag and meta description (breadcrumbs, review stars, sitelinks, etc.).
Google provides two tools to audit structured data on your website: the Schema Markup Validator and the Rich Results Test.
Below are a few examples of local businesses that are benefitting from rich results:
Review Rich Results Example
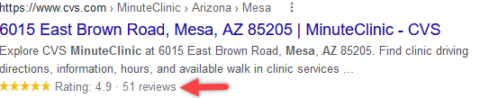 Image from Google, May 2022
Image from Google, May 2022Breadcrumb Rich Results Example
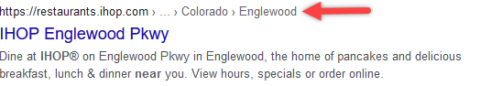 Image from Google, May 2022
Image from Google, May 2022Sitelink Rich Results Example
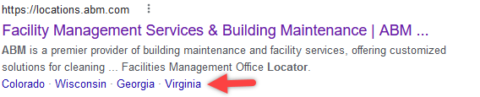 Image from Google, May 2022
Image from Google, May 2022FAQ Rich Results Example
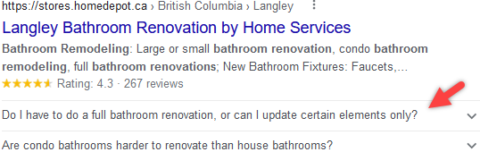 Image from Google, May 2022
Image from Google, May 2022Is Structured Data A Local Ranking Signal?
There has been much debate over the years about whether or not structured data in itself is a search engine ranking signal.
Prominent Google engineer John Mueller has specified more than once that structured data by itself is not a direct search engine ranking signal.
However, structured data indirectly improves search engine visibility through the following means.
Structured Data Helps Search Engine Crawlers Better Comprehend Landing Pages
Properly and thoroughly implemented structured data makes the search crawler’s job easier.
A good analogy would be comparing website properties (content, images, media files, etc.) to a garage full of various boxes and items (snow shovel for the winter, inflatable pool for the summer, etc.).
Let’s say you are having a garage sale and you want visitors (i.e. more website visitors).
It’s Google’s job to advertise your garage sale on the search results pages.
For most websites, Google provides the bare minimum blue title tag and meta descriptions.
However, if your website is properly marked up with structured data then Google may very well reward your websites with a bigger advertisement (i.e. rich results) about your garage sale.
Structured data essentially puts labels on the different objects in your garage making the Google search crawler’s job easier.
Structured Data Improves The Possibility Of Obtaining Rich Results Which Improves Click-through Rates
A rich result is much more eye-catching in the search results and will most likely improve CTR (click-through rates).
The CTR boost can vary depending on what kind of rich result is obtained, for example, FAQ results do very well.
This means your landing page is receiving more traffic because users are seeing relevant snippets about what it contains.
There is also some debate that increased CTR might be a positive SEO signal in itself (signals more engagement & relevancy).
Either way, having an improved CTR means more traffic wherever your website ranks.
What Structured Data Is Recommended For Local Business Websites?
Most local websites have at least some basic structured data enabled.
However, the more thorough and detailed structured data is properly applied the better.
Next, we’ll offer some step-by-step recommendations for how to properly apply structured data:
Select The Best Schema.org Category
Schema.org provides several different schema property options that are uniquely relevant for local businesses.
In order to have necessary local business schema properties (which will be discussed further in detail below), it is imperative to select the most relevant schema category for your local business.
For example, if you are promoting an ice cream chain, the most relevant category is schema.org/IceCreamShop.
If you are trying to promote a local hardware chain then you’d select schema.org/HardwareStore.
Relevant schema categories will help Google better topically understand your website.
What If There Are No Relevant Schema Categories For My Local Business?
If you can’t find a schema.org category that is relevant for your business then the default category should be schema.org/LocalBusiness.
If you’re technically inclined, it is possible to post new schema category recommendations on the schema.org Github forum.
The schema.org developers respond to detailed recommendations on this forum and occasionally create new schema.org properties.
I Selected The Most Accurate Category So What Should I Implement?
After you’ve selected the appropriate category for your business you must have the below schema.org sub-properties to ensure your schema validates.
Errors could disqualify you from obtaining rich results.
The below schema properties are required for validation:
- Url: The URL of the associated landing page.
- Name: Name of the business.
- OpeningHours: Opening and closing hours of a business.
- Telephone: Contact telephone number for the business.
- Image: This can be any relevant image file on your landing page. It is recommended to use a storefront image if that’s available.
- Logo: This should be a link to your business logo image.
- Address: The business address which should be visible on the landing page.
- Geo: This is the geo coordinates of your business location.
- AreaServed: It is recommended to use a zipcode for this schema property.
- MainContentOfPage: Main body content of your landing page.
Common schema properties that are highly recommended:
- Review: A review of your local business.
- AggregrateRating: The overall rating, based on a collection of reviews or ratings, of the item. Make sure to follow Google’s rules on Review Rich Results on this.
- FAQPage: If you have a FAQ page it is imperative to add this specialty schema. Make sure to follow Google’s rules and guidelines.
- AlternateName: Businesses commonly have related names e.g. Acme Stores vs. Acme Inc. The alternateName property marks up other well-known corporate name variations (including abbreviations).
- SameAs: This is a reference to a 3rd party websites that are related to the website’s identity i.e. Facebook pages, Youtube Channel pages, Wikipedia pages, etc.
- HasMap: A URL to the map of your local business.
- Breadcrumb: This schema marks up the existing breadcrumb navigation structure on your website. This schema is highly recommended because it often appears in the SERPS as a rich result.
- Department: Many chain retailers have internal departments (e.g. pharmacies inside grocery stores). This specialty schema helps markup these department stores.
- PriceRange: The price range of the business, for example, $$$.
More advanced schema types:
- Sitelinks Search Box: A sitelinks search box is a quick way for users to do an internal search on your website via the Google SERP vs. visiting your website directly.
- AdditionalType: This is a specialty schema that helps Google understand what your website is topically related to. This can be accomplished by using Wikipedia categories as values for this property. For example, if a local business sells sporting gear it is recommended to have the additionalType property https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sports_equipment.
How Do You Make Sure Your Structured Data Is Validated?
It is very important to make sure your structured data is properly validated.
If it’s not then your landing page will most likely not qualify for rich results.
Google specifically says that if there are error(s): The rich result cannot appear in Google Search as a rich result.
As mentioned earlier there are two different tools to make sure your schema is properly validated: Schema Markup Validator and the Rich Results Test.
Google Search Console also provides enhancement reports on structured data which will be explained in further detail below.
Schema Markup Validator
The Schema Markup Validator enables you to get into the details of structured data itself.
It shows both errors and warnings.
It also allows you to test structured data before it’s enabled on your webpages via pasting code directly into the tool.
Example Of Schema Markup Validator Result
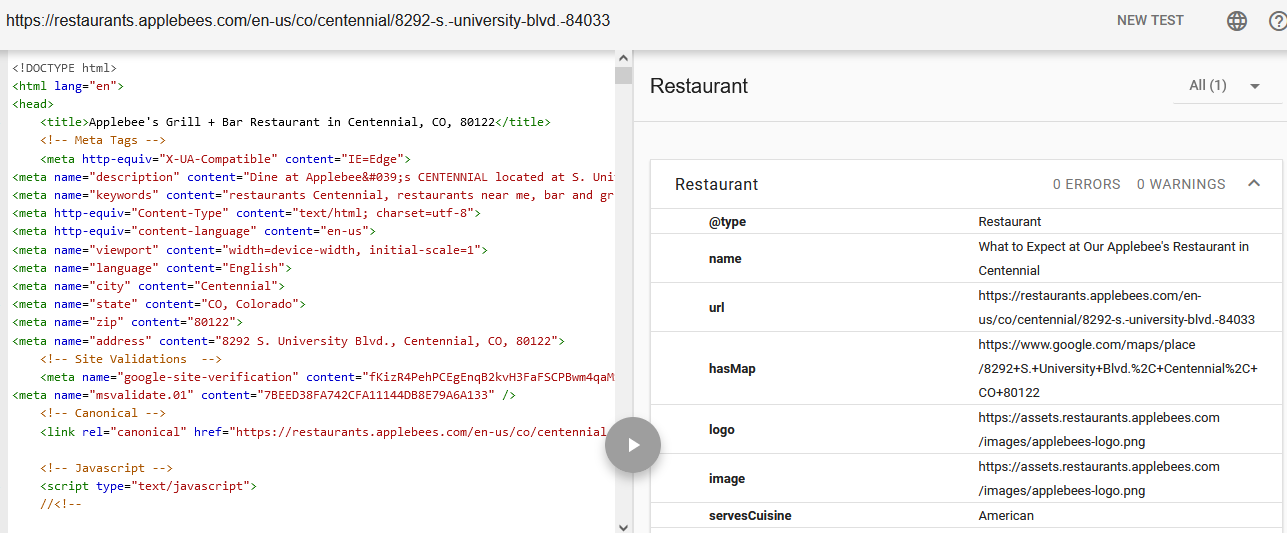 Image from Schema Markup Validator, May 2022
Image from Schema Markup Validator, May 2022Also just to note that while it’s imperative to correct structured data errors you will also often see structured “warnings.”
These warnings are of much lesser concern and Google’s John Muller even mentioned you don’t have to fix all warnings.
A lot of sites have earnings with structured data and that’s perfectly fine.
Rich Results Test
The Rich Results Test is Google’s official tool to see which rich results can be generated by structured data.
This tool also lets you preview how rich results will look in Google SERPs.
Example Of Rich Results Test Preview
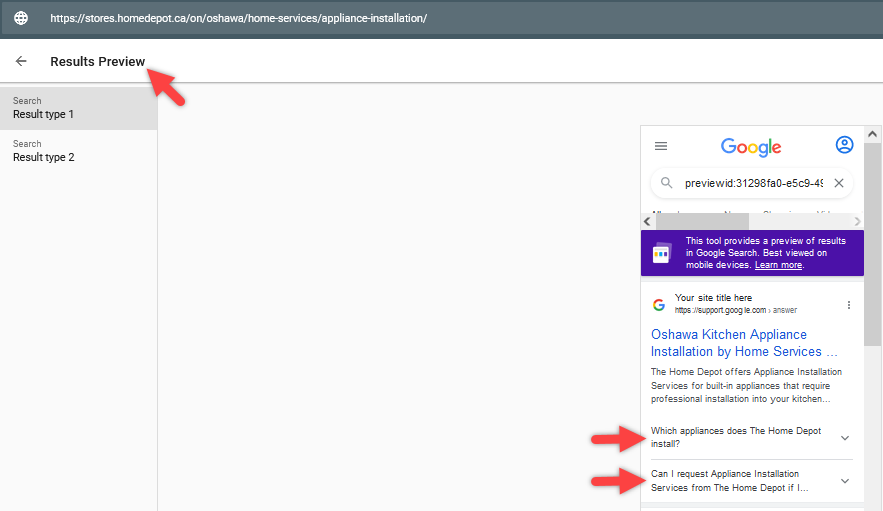 Image from Rich Result test tool, May 2022
Image from Rich Result test tool, May 2022The Rich Result test tool will report structured data errors and warnings as well.
As mentioned earlier, warnings are common and won’t prevent rich results from appearing.
However, structured data errors must be resolved to qualify for rich results.
Structured Data Monitoring Via Google Search Console
Google also offers sitewide structured data monitoring via Google Search Console.
It is highly recommended to have a verified Google Search Console account for your local business website to enable monitoring.
Google Search Console will provide sitewide enhancement reports on how many webpages have validated structured data, warnings, and errors.
Google also sends notification emails if there are issues with structured data on your local business website.
It is recommended to pay attention to these notifications.
Example Of Sitewide Structured Data Report
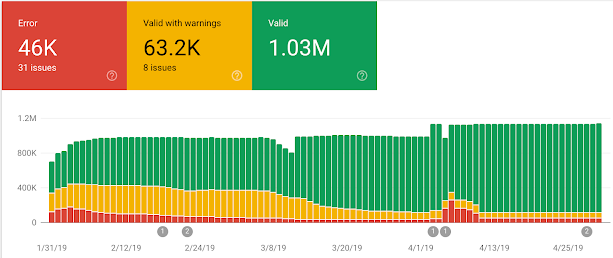 Image from Google Search Console, May 2022
Image from Google Search Console, May 2022How Can I Tell How Many Rich Results My Website Is Getting In The SERPs?
Besides spot-checking rich results, it would be ideal to see how well a local business website is performing across all the Google SERPs.
There are few third-party SEO tools that scrape Google SERPs and provide reports.
One notable tool, Semrush, has a “SERP Feature” report that shows how many aggregate rich results your website is getting.
Example Of Semrush SERP Feature Report
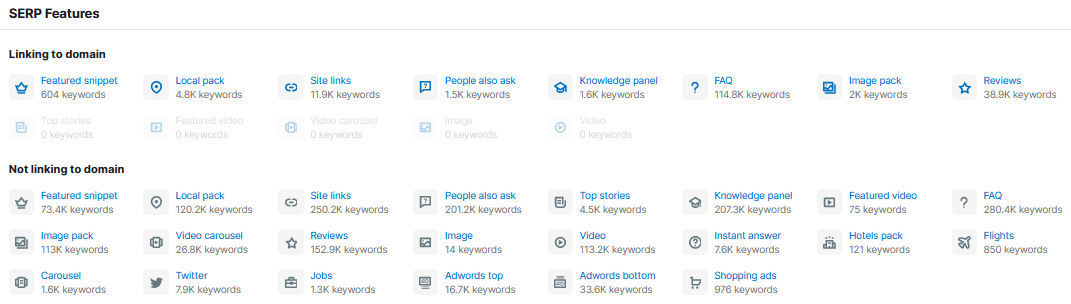 Image from Semrush, May 2022
Image from Semrush, May 2022Is There Anything I Should Avoid When Using Structured Data?
Structured data is meant to be code to label or markup existing properties on your local business website.
Google explicitly requires that your structured data matches what is on the associated landing page.
However, structured data spam does exist and Google can apply manual penalties if they believe a webmaster is egregiously breaking the rules.
Make sure to follow Google’s structured data guidelines carefully.
Conclusion
There is no drawback in applying properly formatted and relevant structured data to your local business’ website.
Also, schema.org is continually coming out with new schema properties along with more integration via Google Search Console.
Most common SEO strategies (meta tag optimization, custom copywriting, design changes, etc.) usually require significant effort and visible on-page website updates.
In comparison, structured data updates are invisible to users visiting your website.
They also don’t require any direct changes to anything on your website besides including a new source code script.
They also have great potential to substantially improve visibility in the Google SERPs via rich results.
If you’re a local business looking to further optimize your website make sure to visit schema.org along with a webmaster to start applying structured data.
More resources:
- Is Schema Stuffing The New SEO Spam?
- Local B2B SEO: The Complete Guide For Local Businesses
- A Guide to Local SEO
Featured Image: Hangouts Vector Pro/Shutterstock




